Visual grounding—localizing objects from natural language descriptions—represents a critical bridge between language and vision understanding. While multimodal large language models (MLLMs) achieve impressive scores on existing benchmarks, a fundamental question remains: can MLLMs truly ground language in vision with human-like sophistication, or are they merely pattern-matching on simplified datasets?
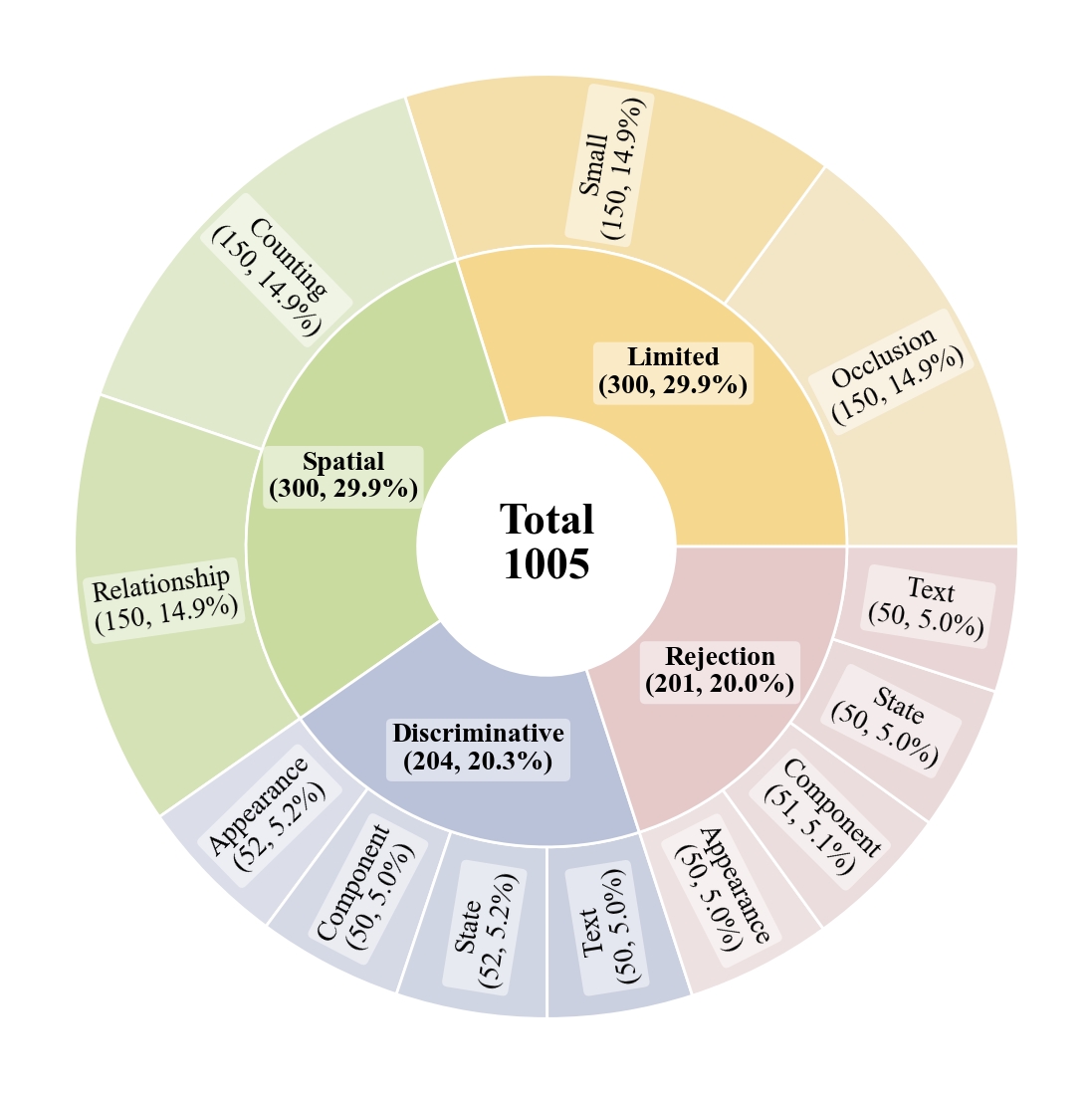
Current benchmarks fail to capture real-world complexity where humans effortlessly navigate ambiguous references and recognize when grounding is impossible. To rigorously assess MLLMs' true capabilities, we introduce GroundingME, a benchmark that systematically challenges models across four critical dimensions:
(1) Discriminative—distinguishing highly similar objects,
(2) Spatial—understanding complex relational descriptions,
(3) Limited—handling occlusions or tiny objects, and
(4) Rejection—recognizing ungroundable queries.
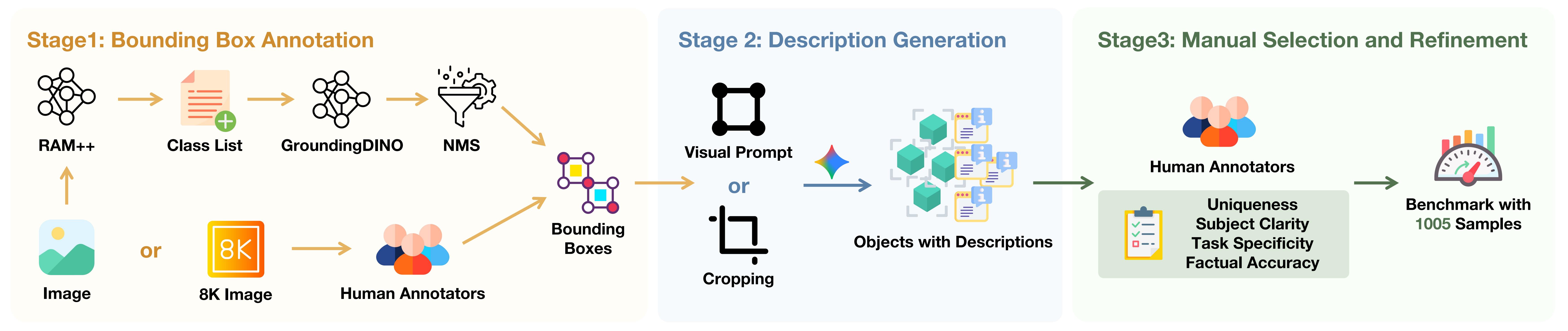
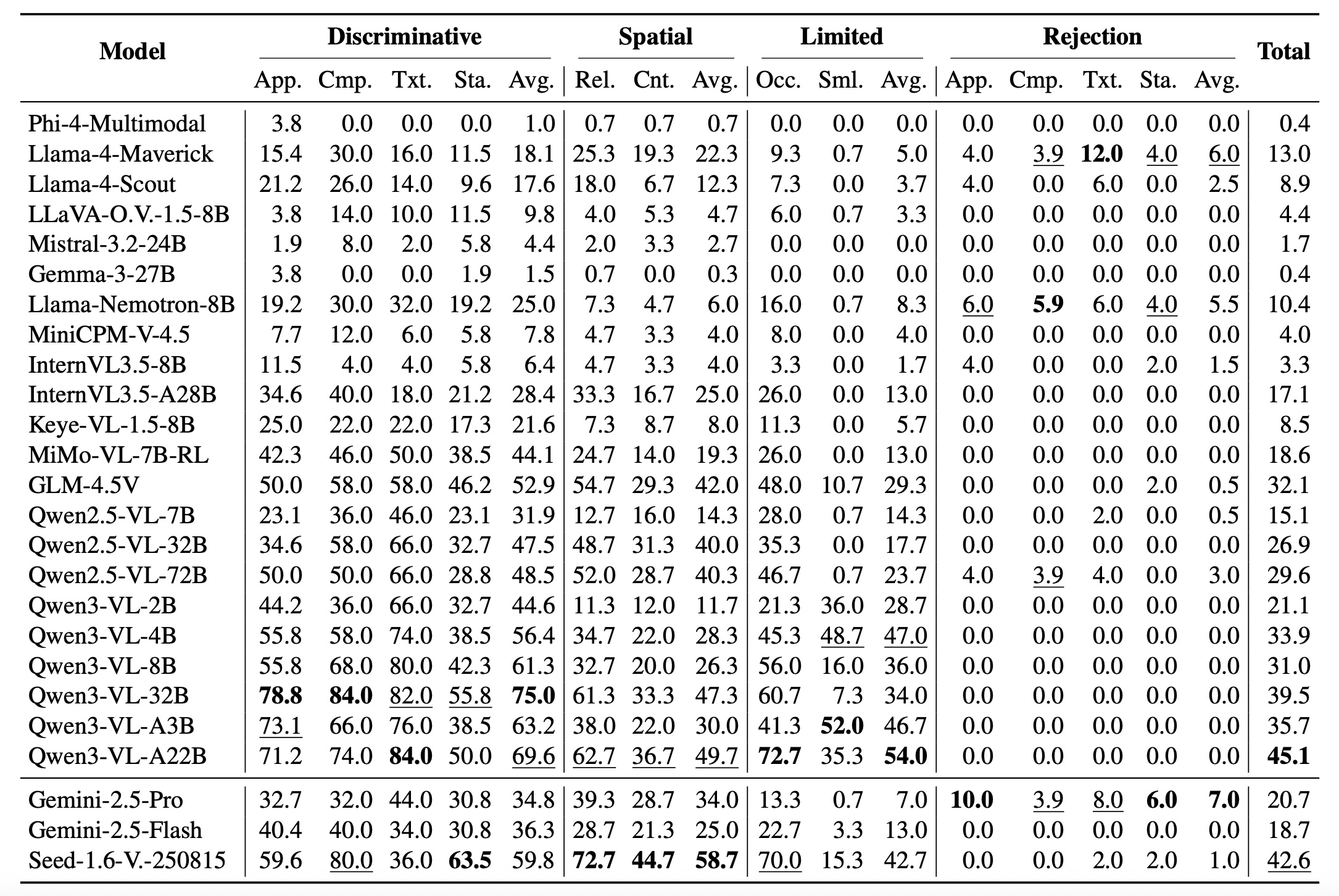
Through careful curation combining automated generation with human verification, we create 1,005 challenging examples mirroring real-world complexity. Evaluating 25 state-of-the-art MLLMs reveals a profound capability gap: the best model achieves only 45.1% accuracy, while most score 0% on rejection tasks—reflexively hallucinating objects rather than acknowledging their absence, raising critical safety concerns for deployment.
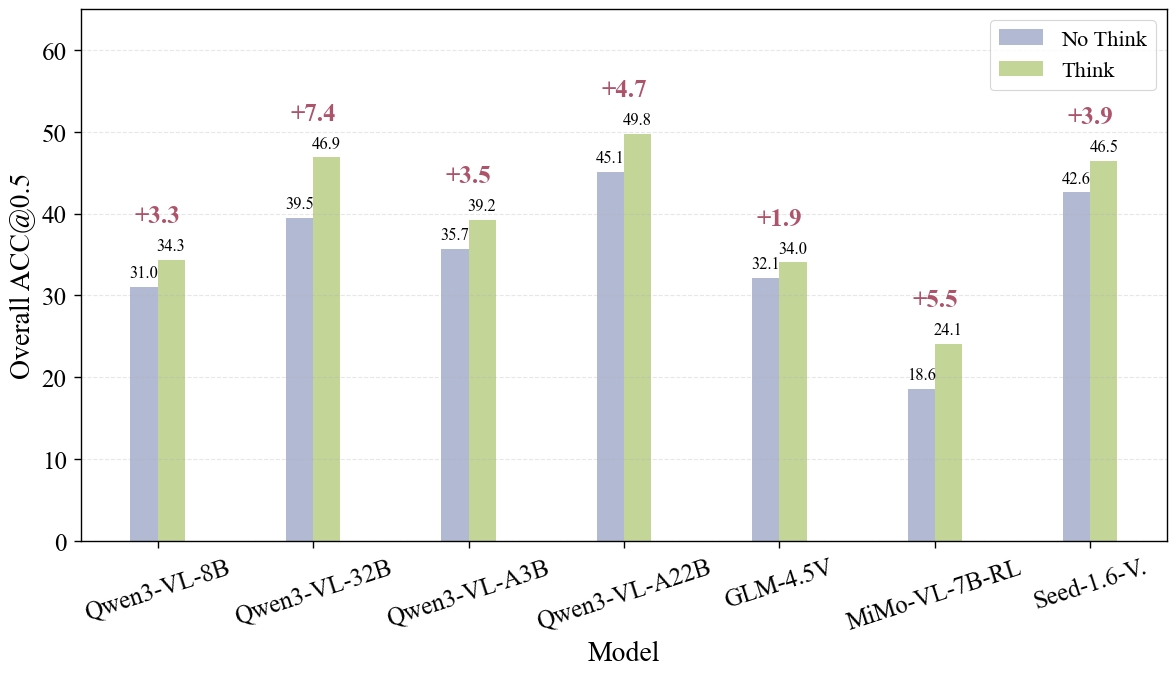
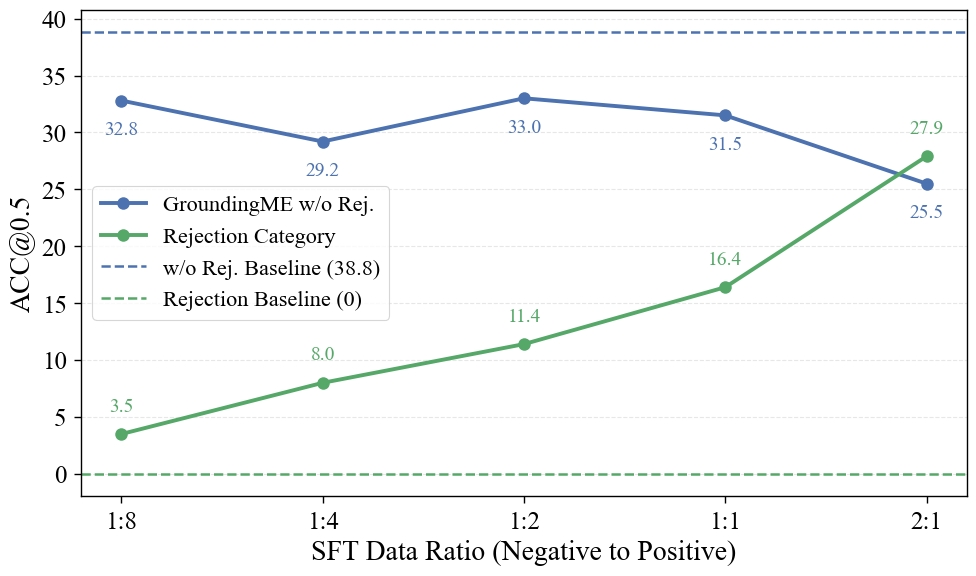
We explore two strategies for improvements: (1) test-time scaling selects optimal response by thinking trajectory to improve complex grounding by up to 2.9%, and (2) data-mixture training teaches models to recognize ungroundable queries, boosting rejection accuracy from 0% to 27.9%. GroundingME thus serves as both a diagnostic tool revealing current limitations in MLLMs and a roadmap toward human-level visual grounding.